
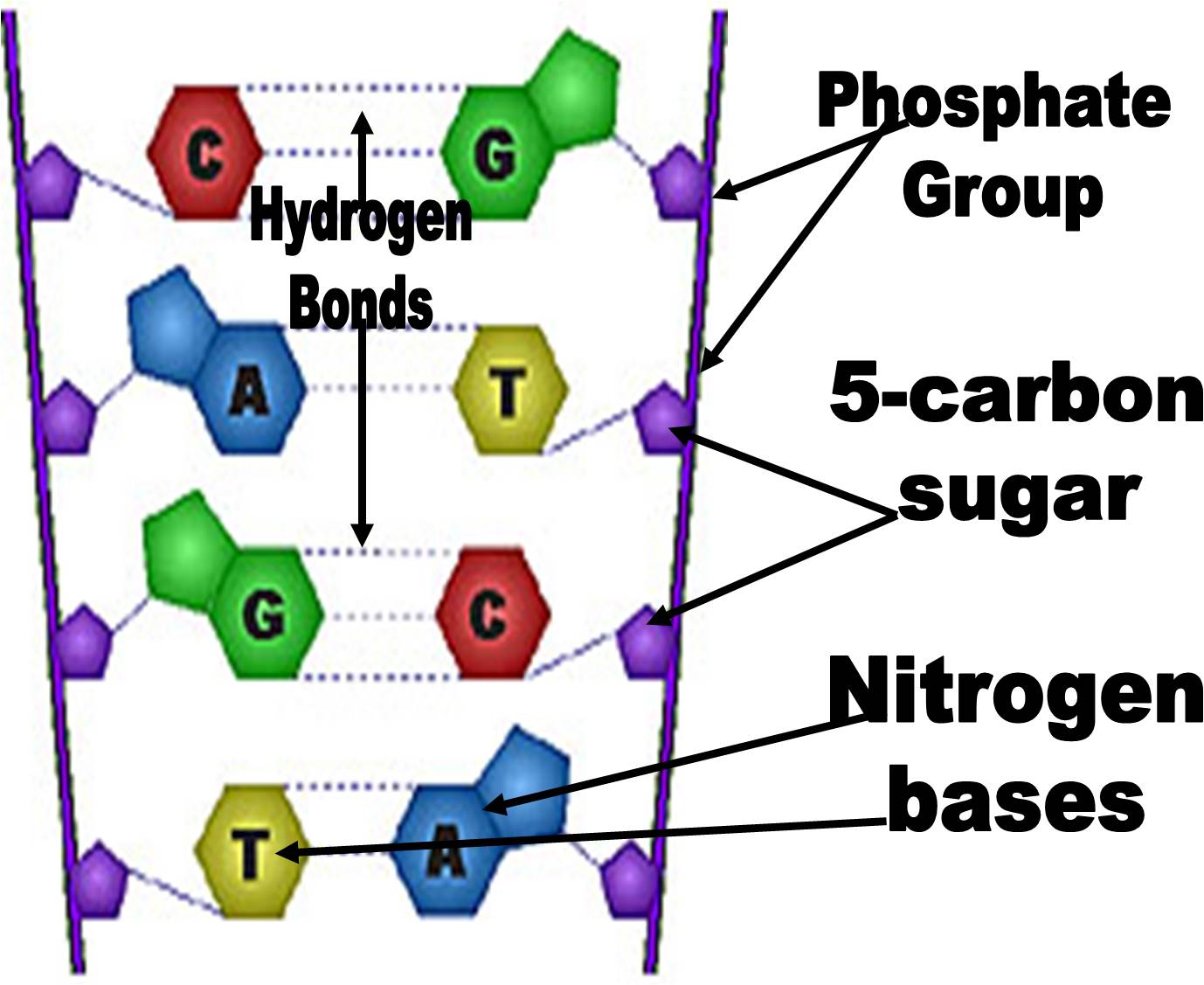
These are given slightly different names:Īnd a nucleotide consists of a nucleoside attached to a (single) phosphate group.ĪMP, CMP, GMP, UMP for the RNA versions - ribonucleotides The names of, or abbreviations for, the 5 (nitrogenous organic) bases in nucleic acids are generally quite well known.Ī nucleoside normally consists of a nitrogenous base section bonded to a pentose sugar. Of course DNA has deoxyribose, and thymine not uracil.ĭo not confuse the base thymine with thiamine - the vitamin (B1) The diagram at the right could be a short section of RNA, or a single strand of DNA. In fact the 3' ends of DNA and RNA molecules have hydroxyl groups (-OH), whereas all the other nucleotides have phosphate groups attached at the 3' position. This process only works in one direction, adding nucleotides to the 3' end of the developing polynucleotide chain. The 3' and 5' labels are important in identifying the ends of nucleic acid strands, and showing the direction of propagation. This is then called a phosphodiester bond, and it is quite a strong linkage but it is flexible and can rotate somewhat so the strand can become curved.Ī polynucleotide is formed when this process is repeated many times.Īs a result, the backbone of DNA and RNA is made up from alternating sugar and phosphate groups which are not easily broken apart. Two nucleotides can join together by forming another covalent bond between a phosphate group and carbon 3' on the next pentose sugar. Interestingly, the bases form a flat section across the middle of the DNA molecule, but thymine's methyl group is the only section that projects somewhat from this.Ī trinucleotide Phosphodiester bonds are shown within green boxes. This would result in a uracil which would cause problems in DNA. In particular, cytosine could become deaminated (and pick up a >O group). It has been suggested that this modification is more suited to DNA's role as a long-term store of information in that error-checking enzymes have evolved to bypass this base (thymine) as they screen for bases which might result from chemical changes which could result in mutations. Thymine is the same as uracil, but with a methyl group off to one side. The O shown in red spans between C1 and C4, forming an ether linkage. ( -OH can make the C3 phosphate bond susceptible to alkaline hydrolysis) Hydroxyl (-OH) groups are the basis for bonds with other groups, formed by condensation reactions:Ĭ1 to the organic base, C5 to the phosphate group.Īnd C3 bonds with phosphate on the next nucleotide ( see below).ĭNA does not have an -OH group at C2, which increases its long-term chemical stability Since DNA strands of the helix run anti-parallel, the direction of the top strand will be 3’ to 5’.Ribose and deoxyribose - possible bonding sitesĬarbon numbers are shown without ' - prime The sugar-phosphate backbone of DNA has the phosphate on the 5’ carbon linked to the 3’ carbon of the next sugar. If the direction of the sugar-phosphate backbone of the bottom strand is 5’ to 3’ from left to right, what is the direction of the top strand from left to right?ĥ’ to 3’ (No, the DNA strands in a helix are anti-parallel.ģ’ to 3’ (No, the sugar-phosphate backbone of DNA is not 3’ to 3’.)ĥ’ to 5’ (No, the sugar-phosphate backbone of DNA is not 5’ to 5’.) Strand are the complement of the nucleotides on the other strand. Nucleotides base pair through hydrogen bonds A pairs with T, and G pairs with C. TACATATGCC (No, this is the reverse sequence, not the complement.)ĪATGCGCACG (No, A does not pair with C and T does not pair with G.) Reading left to right, what is the nucleotide sequence on the other strand of DNA in this section?ĬCGTATACAT (No, this is not the complementary sequence.) This section of DNA has a sequence of nucleotides like this: CCGTATACAT
If you curl the fingers of your right hand in the direction of the helical twists, your thumb (No, The DNA helix does not have evenly spaced coils.)ĭNA is a right-handed double helix. (No, This is a left handed double helix.) The discovery of the structure of DNA was a landmark in molecular biology research.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
